In the battle between future markets and higher market shares, automated systems and artificial intelligence technology is what will decide the winner, taking them ahead of their competitors.
The next decade in AI and ML is expected to turnover 21B Euros worldwide. However, the only possible impediment it needs to address is Data Privacy. As the usage becomes more wide spread, security and privacy aspects of AI & ML are becoming supremely important as people are more conscious and concerned about how their data is being protected and how safe their data actually is.

While the benefits of the advancements are immense, the risks are also increasingly becoming higher. Organizations are constantly working to reduce the future impact of the risks that are being posed. As per a research by Informatica, “by 2025, the data volume is predicted to be 10 times to that of current levels” and this exponential data growth is posing challenges like disparate and diverse form of data – structured, semi-structured and unstructured data; managing large volumes of data for various operations – classification, data extraction, data ingestion, processing, modelling, visualization, etc.
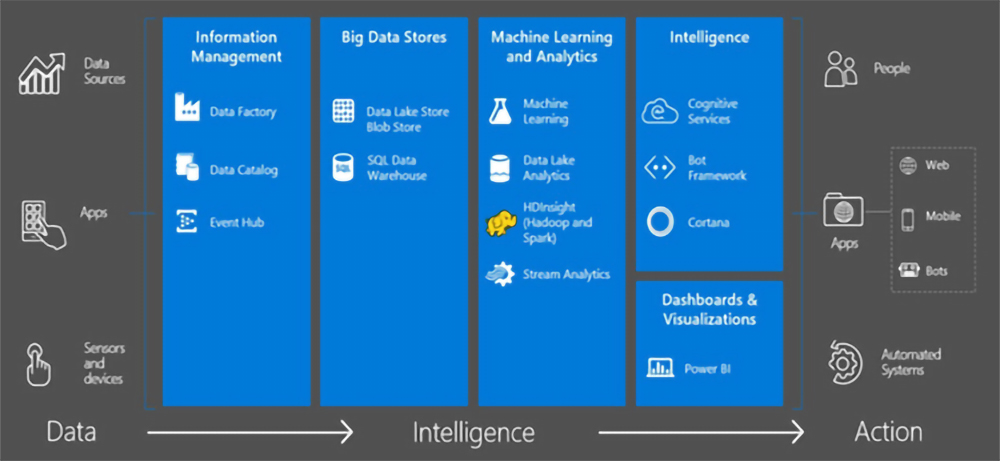
In view of the above mentioned scenarios, information security is critical in managing the flow of data across the value chain of Data Science. Every entity involved is concerned about the privacy /security of data; whether it’s a card holder data (CHD); personally identifiable information (PII); or Quasi Data (QI). The images taken from Azure and Google portals depict the entire workflow of AI and ML.

Data Privacy Norms Around the World

When newer tools, techniques, methodologies and applications are being deployed to address the needs of handling complex data and bringing in intelligence and deploying the solutions in different industry verticals each day, how does one ensure that the concerns of data privacy are addressed?
As a precautionary measure, organizations have to build effective information security frameworks to assure clients and partners of adhering to highest possible levels of standard compliance and an ability to respond effectively in the event of breaches.
The standards in Cybersecurity are sets of best practices for protecting organizations from various types of cyber-attacks. NIST ( National Institute of Standards and Technology) , IASME ( UK based assurance standard for Small and Medium Enterprise Companies ) and RFC ( Request for Comments by The Internet Engineering Force ) are the standards that are adopted globally. In India, we follow the below compliances and certifications predominantly;
ISO 27001: 2013
By providing a set of standard requirements for an Information Security Management System (ISMS), this standard adopts a process-based approach for establishing, implementing, operating, monitoring, maintaining, and improving the ISMS on a continuously. It consists of 14 categories with 114 controls that span across all the risk areas in organizations.
PCI DSS 3.2
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of security standards designed to ensure that all companies accepting, processing, storing or transmitting credit card information maintain a secure environment in processing the data. The standards prescribe 12 domains, that are organized into six control objectives, specific to the storage, transmission and processing of cardholder data.
GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation is a regulation under European Union law on data protection and privacy for all individual citizens of the European Union and the European Economic Area. Under GDPR, organisations need to ensure personal data belonging to individuals are gathered legally and protected against any sort of misuse.
HIPAA
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996) is a legislation in the United States that provides data privacy and security provisions for safeguarding medical information of its citizens. The Act consists of rules governing protected health information (PHI) including Security, Privacy, Identifiers, and Transactions and Code Sets.
India is in the process of implementing data privacy law through the proposed Data Protection Bill that is yet to be approved by its Parliament. Once completed, it would ensure that the PII about citizens of India are well protected, holistically.
The Road to Data Privacy
To achieve the enterprise data intelligence necessary to comply with changing global privacy regulations, organizations can no longer rely on siloed and legacy approaches to finding, analysing, monitoring, and protecting sensitive data. With the threat of sizable fines and the need to maintain customer trust, they urgently need to shift to a new data security paradigm that takes a holistic approach with:
• Centralized data governance management that efficiently handles policy changes and compliance reports
• Continuous sensitive data monitoring and risk analysis that makes it easier to prioritize security programs and investments
• Identity-based intelligence, which provides global and granular analytics of sensitive data based on identity to support data subject access requests and integration with consent management
• Rich, interactive visualizations that provide a complete understanding of data movement both inside and outside the enterprise and between partner and client organizations
• Integrated protection that connects discovery, risk, and monitoring to automated remediation.
What happens next will be decided depending on who gets their act together first—government or enterprises. AI and ML, and the pace in which innovation happens is simply too fast for the law of lands to follow. The next few years is bound to see some restraints, either through the law, AI itself, or other means.
In the years to come, data security is bound to become a critical factor as a part of data science involving AI and ML, as innovations increase the concerns and breaches on privacy of data would be the biggest threats. Leaders would stay focussed in a proactive and preventive approach to protect the data at all times using intelligence, regulations, skillsets and plaforms as Data is the next ‘Gold’.

